The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has just released its October 2025 World Economic Outlook — and the message is clear: while the near-term picture has improved slightly, global growth remains subdued as economies adjust to a complex mix of slowing trade, high borrowing costs, and uneven recovery across regions.
🔗 Read the full report or download full report (PDF)
Key Highlights & Findings
Growth & Inflation Outlook
- The world economy is seen as being in flux, with prospects “dim.”
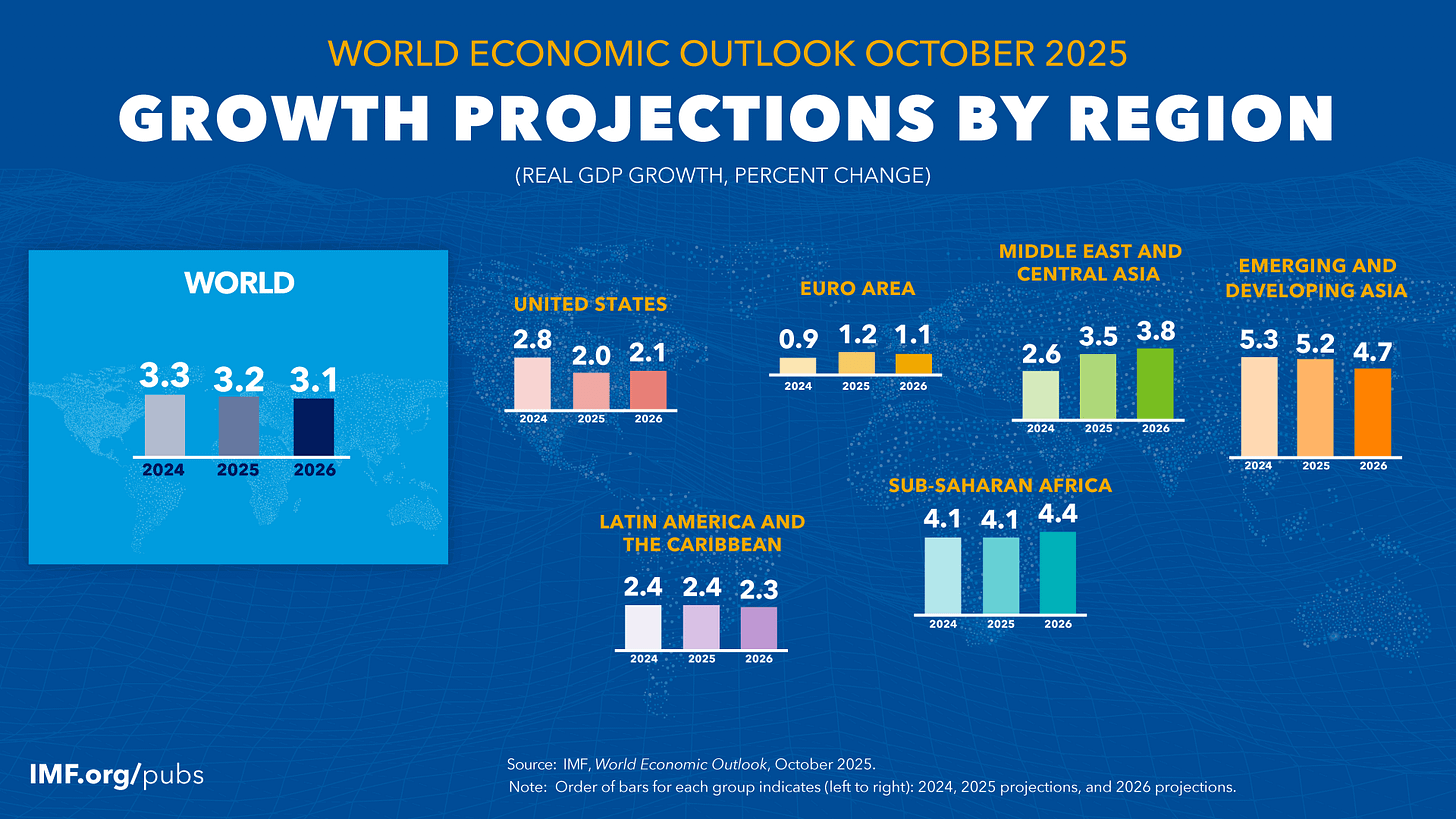
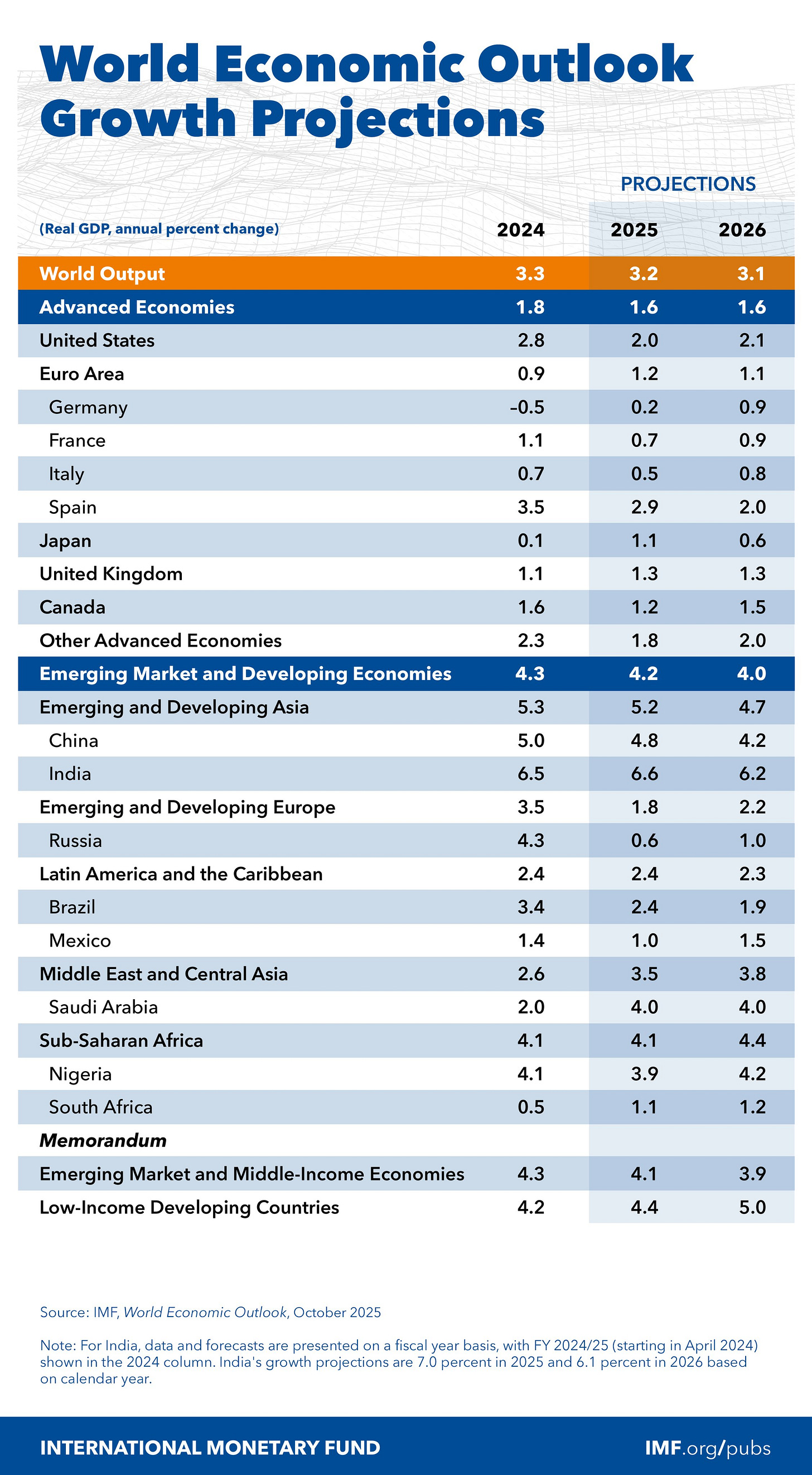
- Global growth is projected at 3.2 % in 2025, down from 3.3 % in 2024, and slowing further to 3.1 % in 2026.
- Advanced economies are forecast to grow by about 1.5 %, while emerging market and developing economies will see just over 4 % growth.
- Inflation is expected to gradually decline in many countries, though it will remain above target in the U.S., with upside risks.
Risks & Vulnerabilities
- The balance of risks is strongly tilted to the downside.
- Threats include:
- Rising protectionism and trade fragmentation
- Policy uncertainty and political instability
- Fiscal vulnerabilities and high public debt
- Financial market corrections, especially if risk premia widen
- Labor supply shocks, especially in aging or low-growth economies
- Erosion of institutional credibility (e.g. loss of central bank independence)
Emerging Markets & Resilience
- Some emerging markets have held up better than expected — due partly to “good luck” in external conditions, but also improved policy frameworks.
- Countries with strong institutional and policy frameworks are in a better position to absorb shocks.
- In weaker economies, delayed monetary tightening or overdependence on foreign exchange interventions may lead to inflation de-anchoring and higher output losses.
Industrial Policy & Trade-Offs
- Chapter 3 evaluates how industrial policy is increasingly being used to build resilience and reduce import dependence.
- But such policies carry trade-offs: potential distortions, fiscal costs, and inefficient resource allocation.
- Their success depends heavily on targeting, institutions, structural reforms, and complementarity with macroeconomic policy.
Policy Recommendations
- Restore confidence through credible, transparent, and sustainable policies.
- Couple trade diplomacy with macroeconomic adjustment.
- Rebuild fiscal buffers and avoid overreliance on debt.
- Safeguard central bank independence and sound institutional frameworks.
- Emphasize structural reforms, especially in weaker economies, to improve resilience.